 Table of Contents
Table of Contents Developer's Manual
Developer's Manual
<?php
$image = new Image('file name');
// for example:
$image = new Image('folder/file.png');
?><?php
$content = file_get_contents('folder/file.png');
$image = new Image($content, 'png');
?><?php
$image = new Image();
$width = 640;
$height = 480;
$image->resize($width, $height);
?><?php
$image = new Image('folder/file.png');
$width = 50;
// if $height is not defined,
// the image is resized proportional
$image->resize($width);
$image->outputToFile('folder/thumbnail.png');
?>
<form method="POST" action="%PHP_SELF%" enctype="multipart/form-data">
(...)
Upload image: <input type="file" name="my_image" />
(...)
</form>
<?php
// get data from form field 'my_image'
$id = 'my_image';
// output to directory 'foo/bar/' using filename 'image'
// (extension will be determined automatically)
$file = 'foo/bar/image';
// output as png image
$type = 'png';
// limit upload to 150 kbyte
$size = 150000;
// resize to 150px x 200px
$width = 150;
$height = 200;
// leave aspect-ratio untouched
$ratio = true;
// set background color to gray
$color = array(80, 80, 80);
// call method
$result = Image::uploadFile($id, $file, $type, $size, $width, $height, $ratio, $color);
// check for errors
if (is_string($result)) {
print "The image was successfully uploaded to '$result'";
// error handling
} else {
switch ($result)
{
case UPLOAD_ERR_SIZE:
case UPLOAD_ERR_INI_SIZE:
case UPLOAD_ERR_FORM_SIZE:
die('File too big!');
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_NO_FILE:
die('No file has been uploaded!');
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_INVALID_TARGET:
die("Unable to write to file: '$file'");
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_FILE_TYPE:
die('The file is not a recognized image!');
break;
default:
die('Some unexpected error occurred!');
break;
}
}
?><?php
// create an empty image
$image = new Image();
$width = 180;
$height = 120;
$image->resize($width, $height);
// set line width to 3px (optional)
$image->setLineWidth(3);
// fill canvas with background color
$x = 0;
$y = 0;
$image->fill($image->white, $x, $y);
// draw a line
$x1 = 10;
$y1 = 10;
$x2 = 100;
$y2 = 30;
$image->drawLine($x1, $y1, $x2, $y2, $image->black);
// draw a circle
$x = 30;
$y = 50;
$width = 50;
$image->drawEllipse($x, $y, $width);
// draw a rectangle
$x = 10;
$y = 60;
$width = 100;
$height = 50;
$border = $image->black;
$fill = $image->navy;
$image->drawRectangle($y, $y, $width, $height, $border, $fill);
// draw a triangle (or other polygon)
$points = array(
0 => array( 20, 0 ),
1 => array( 40, 20 ),
2 => array( 0, 20 )
);
$x = 50;
$y = 80;
$border = $image->black;
$fill = $image->yellow;
$image->drawPolygon($points, $x, $y, $border , $fill);
// write a text
$text = 'Hello World';
$x = 70;
$y = 40;
$color= $image->black;
$image->drawString($text, $x, $y, $color);
// Use of brushes
// create new brush
$brush = new Brush('small star');
// set brush size to 10px
$brush->setSize(10);
// set brush color to red
$brush->setColor(255, 0, 0);
// select the brush
$image->setBrush($brush);
// draw a dot using the brush
$x = 150;
$y = 100;
$image->drawPoint($x, $y, IMG_COLOR_BRUSHED);
// output file to browser
$image->outputToScreen('png');
exit;
?> 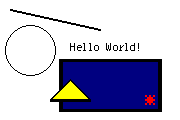
Figure: Script output
If you work with images, you need colors to draw lines, text or surfaces.
There are 17 predefined colors. These are:
You can get other colors by calling: $color = $image->getColor($red, $green, $blue); where $red, $green, $blue are integers between 0 and 255.
It is important to you understand, that a color is not an object by itself, but a specific property of a graphic. This is, each image has its own color palette and each color is a part (mathematically speaking an "element") of this palette.
The palette of the image is an indexed set of all contained in the graphic colors. A color is represented by an integer. To be more precise: it is the index number of this color within the color palette of the image. This means, number 1 names the color, which is stored at position 1 of the image's color palette. For example, this color might be "red" in this image. However, you should note, that depends on the color palette and differs from one image to another.
Here is a list with examples for some interesting methods of the class image:
<?php
$image = new Image('foo.png');
/* set brightness
*
* integer of -1.0 trough +1.0 (-100% and +100%)
*/
$amount = 0.5; /* 0.5 = +50% */
$image->brightness($amount);
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* set contrast
*
* integer of -1.0 trough +1.0 (-100% and +100%)
*/
$amount = 0.5; /* 0.5 = +50% */
$image->contrast($amount);
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* blur the image
*
* integer of 0.0 trough +1.0 (0% and +100%)
*/
$amount = 0.8; /* 0.8 = 80% */
$image->blur($amount);
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* sharpen the image
*
* integer of 0.0 trough +1.0 (0% and +100%)
*/
$amount = 0.8; /* 0.8 = 80% */
$image->sharpen($amount);
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* set to 256 colors grayscale palette
*/
$image->toGrayscale();
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* colorize the image
*
* $red, $green, $blue = integer -255 through 255
*
* the given color value is added to colors of the image
*/
$red = -80;
$green = -40;
$blue = 120;
$image->colorize($red, $green, $blue);
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* multiply
*
* $red, $green, $blue = integer 0 through 255
*
* the given color value is multiplied to the colors of the image
*/
$red = 100;
$green = 255;
$blue = 50;
/* this examples reduces the red- and clue channels */
$image->multiply($red, $green, $blue);
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* monochromatic filter
*
* $red, $green, $blue = integer 0 through 255
*
* Colorized the image using the given color.
*/
$red = 130;
$green = 180;
$blue = 200;
$image->monochromatic($red, $green, $blue);
?> 
Figure: Script output
<?php
/* invert color values (negate)
*/
$image->negate();
?> 
Figure: Script output
For more details and examples see the API documentation.
 Thomas Meyer, www.yanaframework.net
Thomas Meyer, www.yanaframework.net